Kartini Reactor Control
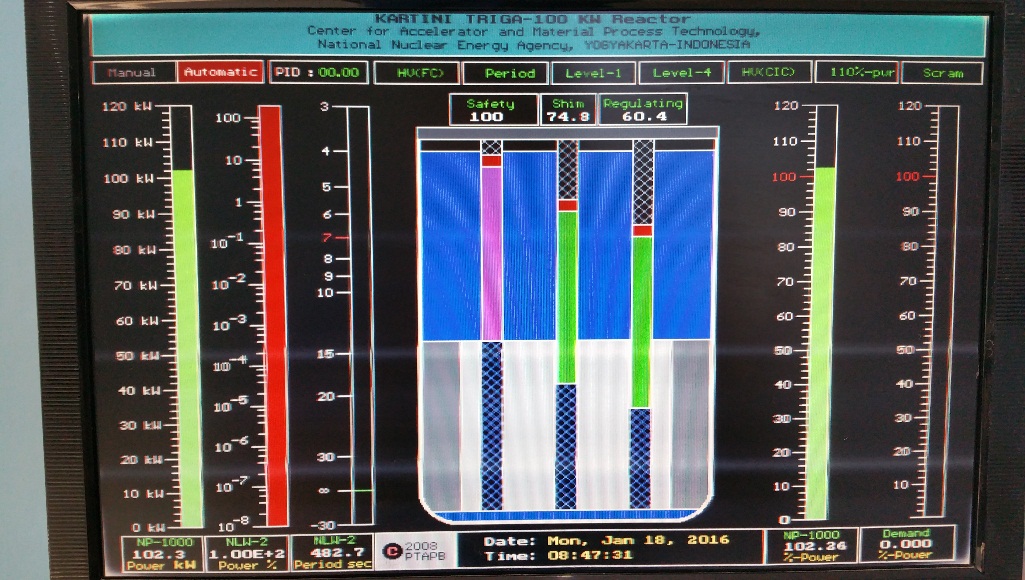
Reactivity control systems are designed and installed for the circumstances normal operation and shutdown of the reactor. The reactivity control function is divided into three parts: reactive controls for regulating rods of reacting shift rods and reactivity controls as safety rods each by inserting rods of strong neutron absorber materials at a particular position on the core reactor. The position is the safety bar occupying the position in the C-5 ring, the compensation rod occupies the position of the C-9 ring and the adjusting rod occupies the position of the E-1 ring. The compensation and regulating rods are Aluminum tube containing Boron Carbide powder (B4C), while the safety bar contains graphite and boral. The diameter of the control rods is 2.2 cm respectively, 3.2 cm compensation and 2.5 cm of protection with each length is 51 cm.
Full reactivity is done by adjusting the length of the insertion of the control rod inside the core. The length of the insertion path of the entire control rod is 38 cm. To keep track of the passage inside the core each control rod inserts the porch through the guide rod that pierces the core from the top core grille to the lower core grille. The steering rods are made of hollow aluminum for the water way.
Control rod motion is controlled by using a rod that connects the control rod with a driving motor instrument located above the reactor tank. Each control rod has a separate drive motor.
The scaffolding facility of the reactor (scram system) is provided by removing the free falling control rods inserted in the core through the instrumentation of the beam located on the connector between the control rod and the instrumentation of the driving motor.
The purpose of reactivity control function is:
- providing the operator with the necessary reactor power control,
- to shutdown the reactor and maintain subcritical state,
- limiting the insertion of reactivity,
- preventing core damage due to reactivity effect
- automatically retains the reactor power at the desired power level by the operator.
In relation to the safety of the reactor, the reactor control system is designed in such a way that in case of failure of operation (eg failure of reactivity, power outages, failure of cooling etc.), the automatic reactor will be extinguished. So it can be said the reactor failed operation but all the system is safe.
In relation to the safety of the reactor, the reactor control system is designed in such a way that in case of failure of operation (eg failure of reactivity, power outages, coolant failure etc.) the automatic reactor will be extinguished/suspended. So it can be said the reactor failed operation but all the system is safe.
The reactor blackout capability is maintained in a way:
- carry out control rod calibration periodically 2 times a year or every change of core arrangement
- keep the amount of fuel load in such a way that the shutdown margin value is still greater than the minimum limit set.

 I R L
I R L 


